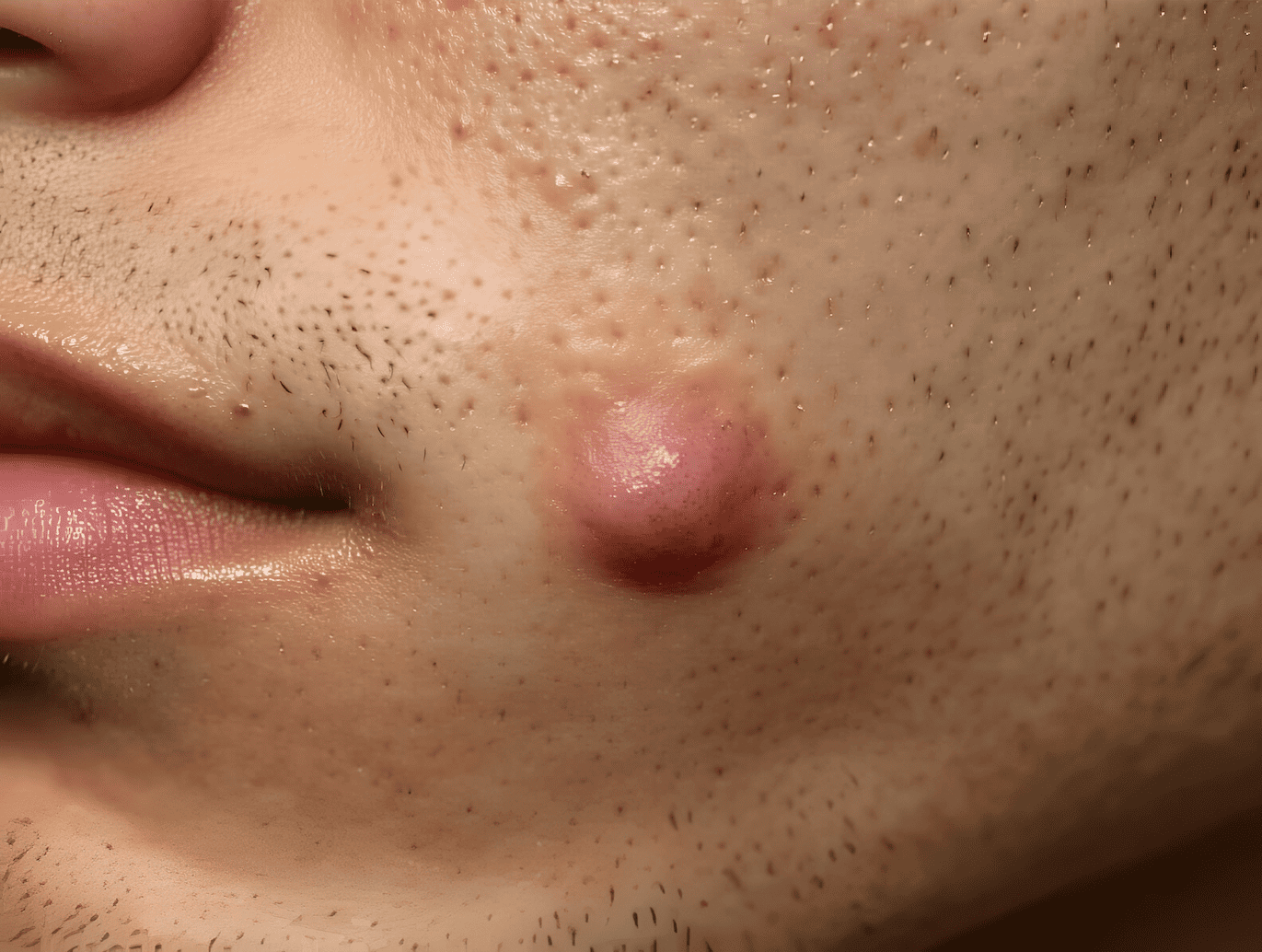An abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to an infection, often caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. These infections trigger the body’s immune response, leading to the accumulation of dead tissue, white blood cells, and bacteria, which collectively form pus. Abscesses can develop anywhere in the body, including the skin, internal organs, and even the brain. If left untreated, they can cause severe complications. This article explores the types, symptoms, and treatment options for abscesses.
What is an Abscess?
An abscess is a localized collection of pus caused by an infection. It forms when the body’s immune system tries to fight off bacteria or other pathogens. Pus consists of dead tissue, white blood cells, and bacteria. Abscesses can occur on the skin (e.g., boils) or internally (e.g., liver or brain abscesses).
Common Types of Abscesses
- Skin Abscess (Boil):
- Forms under the skin, often around hair follicles.
- Symptoms include swelling, redness, pain, and warmth in the affected area.
- Anal Abscess:
- Develops near the anus due to infected anal glands or sexually transmitted infections.
- Symptoms include painful swelling, redness, and warmth.
- Bartholin’s Abscess:
- Occurs in the Bartholin’s glands near the vagina.
- Caused by infections from bacteria like E. coli or STIs.
- Brain Abscess:
- A rare but serious condition caused by infections spreading from nearby areas (e.g., sinusitis or ear infections).
- Symptoms include severe headaches, fever, and neurological issues.
- Dental Abscess:
- Forms in the teeth or gums due to poor oral hygiene.
- Symptoms include severe tooth pain, swelling, and sensitivity.
- Liver Abscess:
- Can be amoebic (caused by parasites) or pyogenic (caused by bacteria).
- Symptoms include abdominal pain, fever, and jaundice.
- Spinal Abscess:
- A rare but life-threatening condition often caused by bacterial infections.
- Symptoms include back pain, fever, and neurological deficits.
Symptoms of an Abscess
- Swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected area.
- Pain or tenderness.
- Fever and chills (in severe cases).
- Pus drainage (in skin abscesses).
- Systemic symptoms like fatigue or malaise (for internal abscesses).
Causes of Abscesses
- Bacterial infections (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus).
- Parasitic infections (e.g., Entamoeba histolytica).
- Blocked glands or hair follicles.
- Poor hygiene or untreated infections.
Treatment Options
- Drainage:
- The primary treatment for skin abscesses involves draining the pus.
- Antibiotics:
- Prescribed to treat bacterial infections.
- Surgery:
- Required for internal abscesses (e.g., liver or brain abscesses).
- Pain Management:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort.
Prevention Tips
- Maintain good hygiene.
- Treat infections promptly.
- Practice safe sex to avoid STIs.
- Follow a healthy oral care routine.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if you notice:
- Persistent pain or swelling.
- Fever or chills.
- Symptoms of an internal abscess (e.g., abdominal pain or neurological issues).