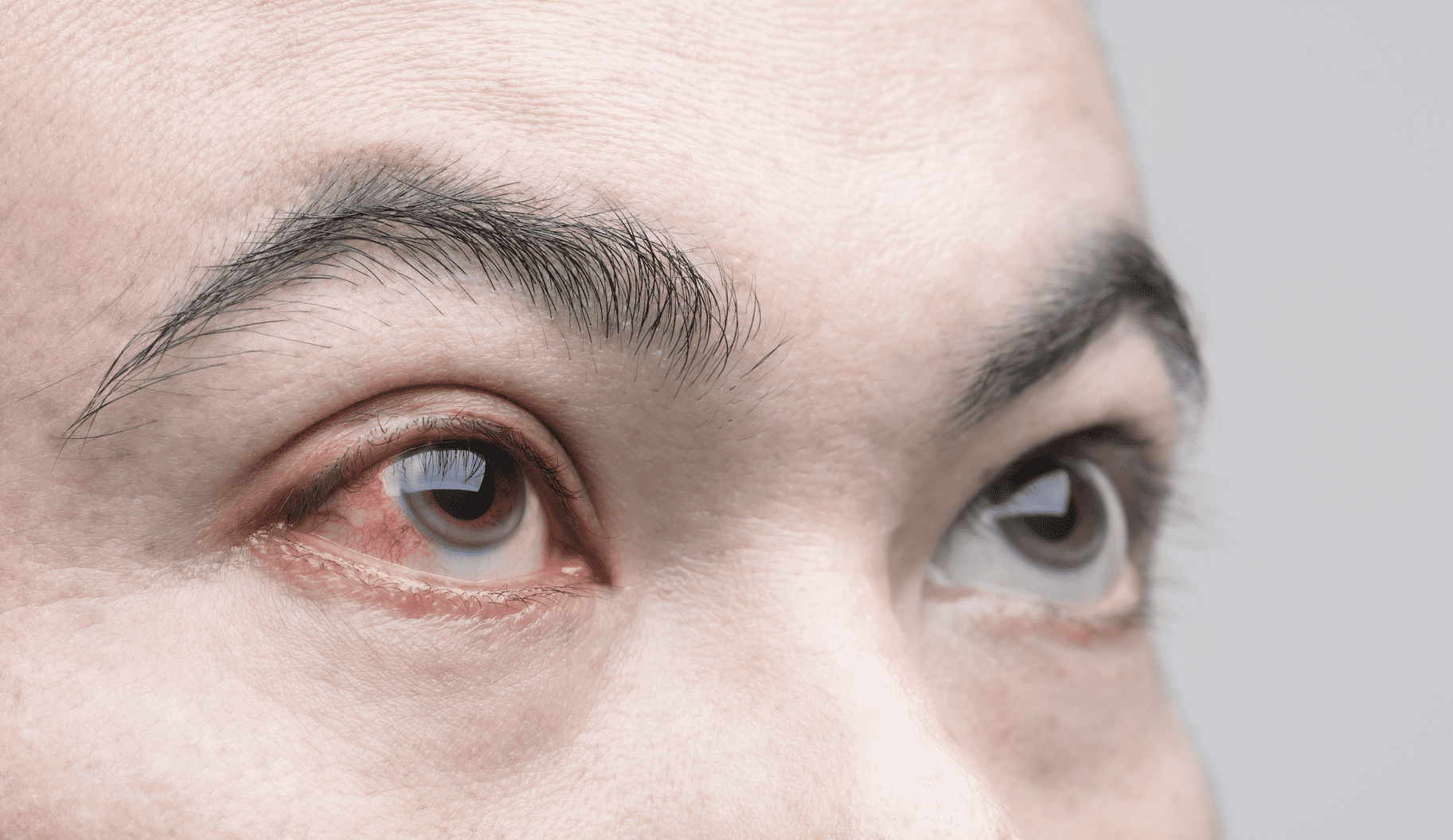
Corneal abrasion refers to a small scratch on the clear, protective layer of the eye that covers the iris and pupil. This condition can cause discomfort, redness, excessive tearing, and sensitivity to light. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent further damage to the eye.
The cornea, the outermost layer of the eye, is rich in nerve cells, making it highly sensitive. Even a minor scratch can lead to significant discomfort and a persistent feeling of having something in the eye.
Causes of Corneal Abrasion
Corneal abrasions can occur due to various reasons, including:
- Exposure to dust, dirt, sand, wood shavings, metal particles, or even a piece of paper.
- Accidental poking of the eye with fingernails, pens, or makeup tools.
- Chemical injuries from substances entering the eye.
- Rubbing the eyes too hard.
- Overuse of contact lenses or wearing dirty or ill-fitting lenses.
- Complications from eye infections.
- High-risk activities like swimming, welding, or cutting metal without protective eyewear.
Certain conditions can also increase the risk of corneal abrasion, such as:
- Dry eyes.
- Inability to fully close the eyelids during sleep.
- A history of corneal abrasions or eye injuries.
- Genetic corneal disorders, such as corneal dystrophy.
How to Treat Corneal Abrasion
If you suspect a corneal abrasion, avoid rubbing your eyes, as this can worsen the scratch. Instead, follow these steps:
- Rinse your eyes with clean, running water, especially if exposed to chemicals.
- Blink several times to remove small particles like dust or sand.
- Avoid using eye drops or any substances without medical advice.
- Refrain from wearing contact lenses during the healing process.
- Avoid applying makeup around the eyes.
- Do not attempt to remove any foreign object stuck in the eye.
- Avoid touching the eyeball with cotton swabs, tweezers, or any tools.
- Wear sunglasses outdoors to protect your eyes from sunlight.
- Use protective goggles during high-risk activities like welding or cutting metal.
Most corneal abrasions heal within 1–2 days with proper care. However, untreated abrasions can lead to infections, corneal ulcers, or even vision loss.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist, such as sudden eye pain, redness, excessive tearing, light sensitivity, or a feeling of something in the eye, seek medical attention immediately. A doctor can remove any foreign objects, prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointments, and prevent complications.
Prevention Tips
- Always wear protective eyewear during high-risk activities.
- Keep your contact lenses clean and avoid overusing them.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes, especially with dirty hands.
- Treat dry eyes with artificial tears if necessary.
Corneal abrasions may seem minor, but they require proper care to avoid serious consequences. Protect your eyes and seek professional help if needed.