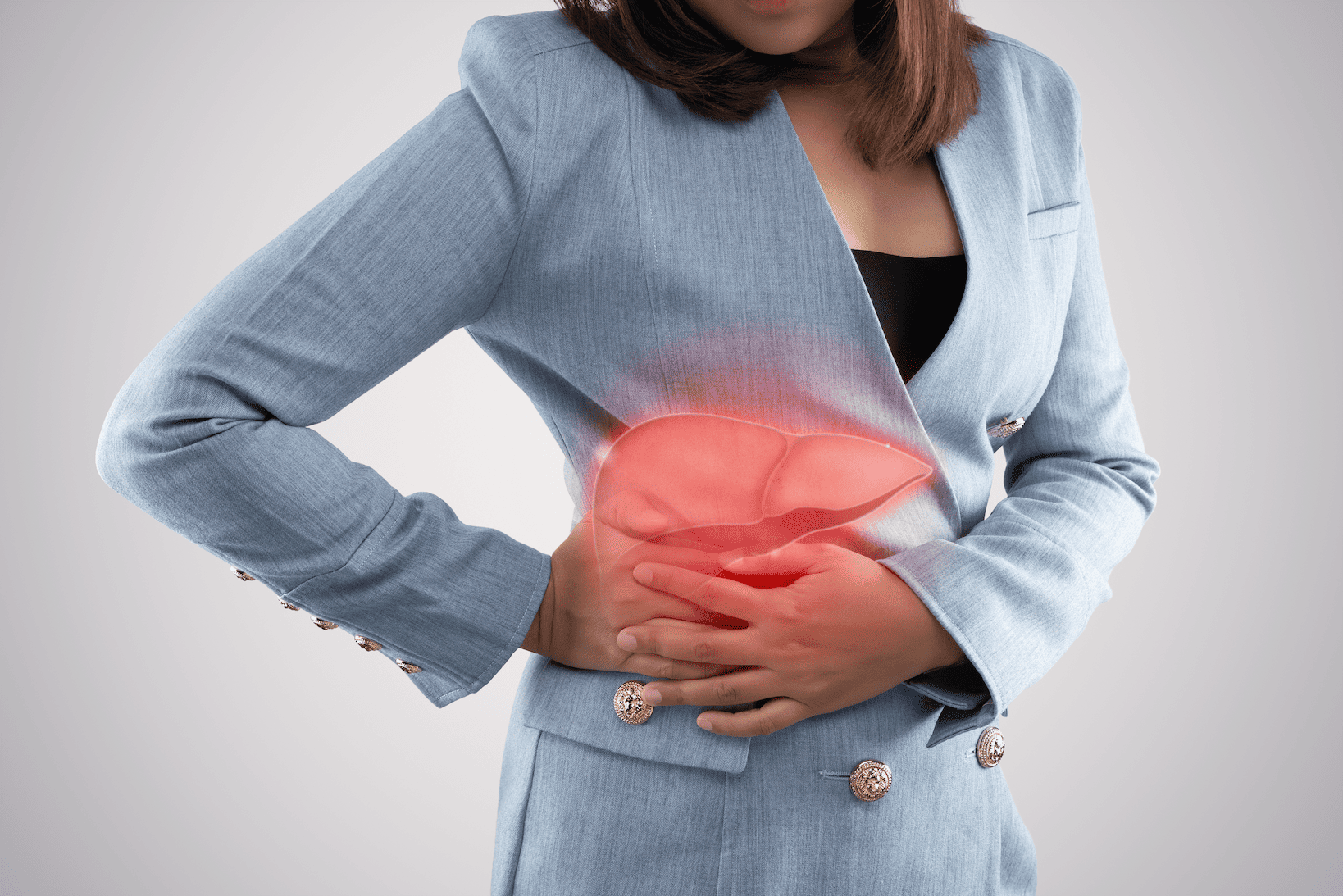
A liver abscess is a serious condition characterized by the accumulation of pus in the liver due to infection. This condition requires immediate medical attention as it can lead to life-threatening complications. The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous functions, including detoxification, protein production, bile secretion, and blood clotting. When infected, its ability to perform these functions is compromised, posing significant health risks.
Types of Liver Abscess
Liver abscesses are categorized based on their causes:
- Pyogenic Liver Abscess
Caused by bacterial infections, this is the most common type. It can result from conditions like appendicitis, gallbladder infections, sepsis, or trauma to the liver. - Amebic Liver Abscess
This type is caused by the parasite Entamoeba histolytica, commonly found in areas with poor sanitation. It often follows amebic dysentery. - Fungal Liver Abscess
Rare and typically affecting individuals with weakened immune systems, this type is often caused by Candida species.
Symptoms of Liver Abscess
Common symptoms include:
- Pain in the upper right abdomen
- Fever and chills
- Night sweats
- Digestive issues like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the risk of developing a liver abscess:
- Age over 70
- Poor sanitation and hygiene
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Malnutrition
- Weakened immune system due to conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer
- Recent medical procedures, such as bile duct endoscopy
Diagnosis and Treatment
Doctors diagnose liver abscesses through physical exams, blood tests, and imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI. Treatment typically involves:
- Antibiotics or Antifungal Medications: Administered intravenously to combat the infection.
- Drainage: A minimally invasive procedure to remove pus using a catheter guided by imaging.
- Surgery: Required in severe cases to remove the abscess.
Complications
If left untreated, liver abscesses can lead to severe complications such as sepsis, peritonitis, or pericarditis, which can be fatal.
Prevention
Maintaining good hygiene, avoiding contaminated food and water, and managing underlying health conditions can help reduce the risk of liver abscesses.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience symptoms like persistent abdominal pain, fever, or jaundice, seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a full recovery.
Gb Stock photos by Vecteezy