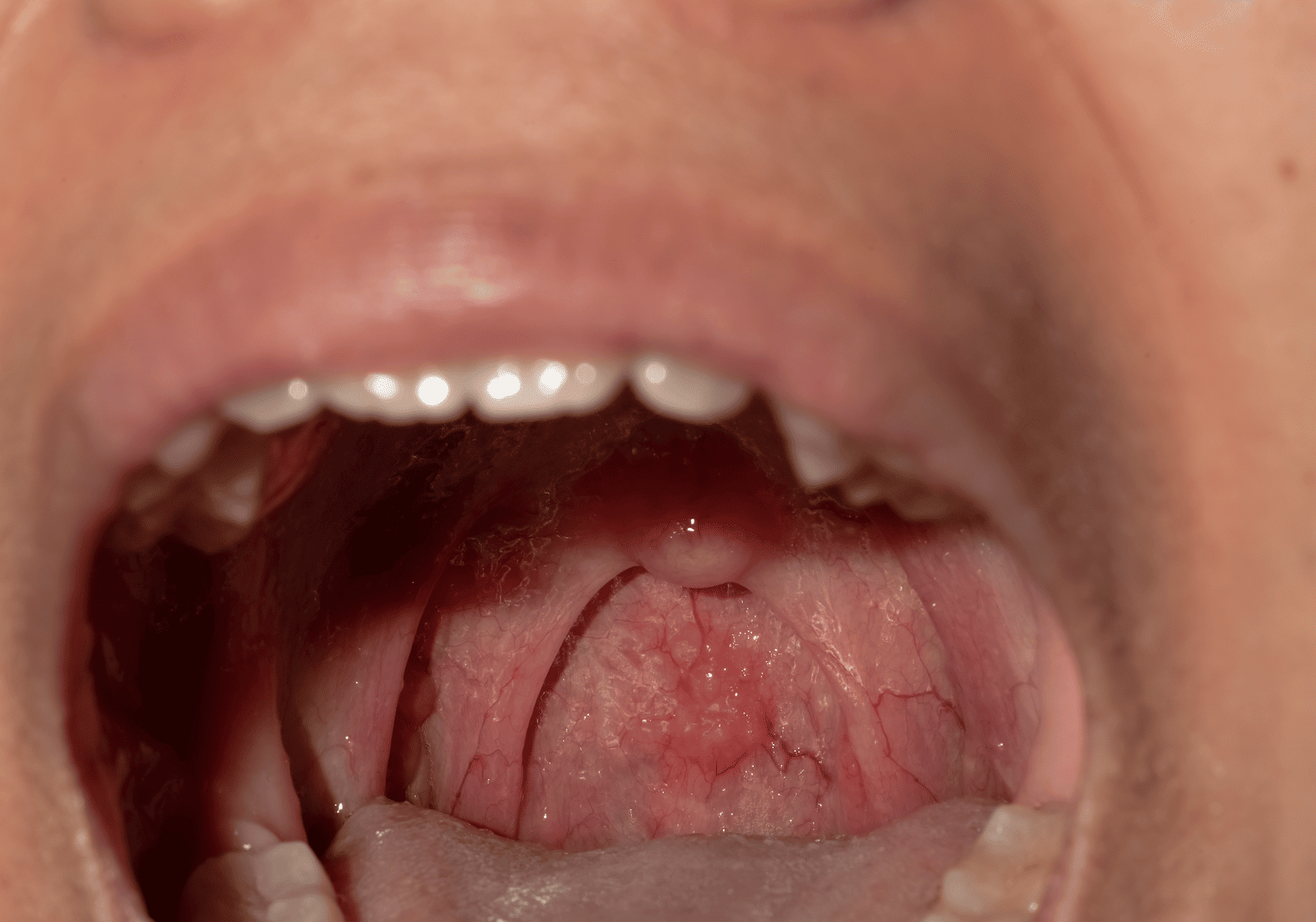
A peritonsillar abscess is a bacterial infection that leads to the formation of pus around the tonsils. This condition often arises as a complication of untreated or poorly managed tonsillitis. It primarily affects children, teenagers, and young adults, causing severe throat pain, swelling, and difficulty in swallowing, speaking, and even breathing. If left untreated, it can lead to life-threatening complications.
What Causes a Peritonsillar Abscess?
The most common cause of a peritonsillar abscess is the same bacteria responsible for strep throat, particularly Streptococcus. These bacteria can spread from infected tonsils to surrounding tissues. Other risk factors include:
- Chronic tonsillitis
- Gum infections like periodontitis or gingivitis
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Smoking habits
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Tonsil stones (tonsilloliths)
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for timely treatment. Common signs include:
- Severe sore throat, usually on one side
- Fever and chills
- Ear pain on the affected side
- Difficulty opening the mouth or swallowing
- Swelling in the face or neck
- Hoarse voice
- Shifting of the uvula to one side
- Swollen and tender lymph nodes in the neck
In severe cases, the abscess can block the airway, leading to a medical emergency. If the abscess ruptures, pus can spread to the lungs, causing pneumonia, or infect surrounding tissues, resulting in phlegmon.
How Is a Peritonsillar Abscess Treated?
Immediate medical attention is essential. A doctor will typically perform a physical examination of the mouth, throat, and neck. Blood tests or imaging studies like CT scans or ultrasounds may be used if necessary.
Treatment options include:
- Medical Procedures:
- Needle Aspiration: Draining the pus with a needle.
- Incision and Drainage: Making a small cut to allow pus to drain.
- Tonsillectomy: Surgical removal of the tonsils, especially for recurrent cases.
- Medications:
- Antibiotics to combat the bacterial infection.
- Pain relievers to manage discomfort.
- Intravenous fluids and nutrition if swallowing is too painful.
It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance.
Prevention Tips
Maintaining good oral hygiene, avoiding smoking, and treating throat infections promptly can help prevent peritonsillar abscesses. If you experience symptoms, seek medical care immediately to avoid complications.
Gb Stock photos by Vecteezy